What KoZiBu is
 The KoZiBu functionalities described in this web page are not necessary implemented in the current prototype version : only the "converter file" module and partially the "building explorer" are currently available. In fact KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa and the functionalities envisaged will be developed little by little.
The KoZiBu functionalities described in this web page are not necessary implemented in the current prototype version : only the "converter file" module and partially the "building explorer" are currently available. In fact KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa and the functionalities envisaged will be developed little by little.
 KoZiBu is a design tool on classical PC for buildings dynamic thermal simulation and it's aimed for design offices, teaching and research organisms. The current version may be downloaded for free
KoZiBu is a design tool on classical PC for buildings dynamic thermal simulation and it's aimed for design offices, teaching and research organisms. The current version may be downloaded for free
 KoZiBu is designed to be multi-languages but currently only French and English are fully implemented, and texts in German, Italian and Spanish are partially translated.
KoZiBu is designed to be multi-languages but currently only French and English are fully implemented, and texts in German, Italian and Spanish are partially translated.
What KoZiBu is designed for
 KoZiBu is a software used to analyze dynamic hygrothermal performance of building. It is aimed to conduct studies of heating and cooling strategy, air conditionning or ventilation options, insulating materials to be installed. The main objective of KoZiBu is to forecast the energy consumption, and temperature and humidity evolution range.
KoZiBu is a software used to analyze dynamic hygrothermal performance of building. It is aimed to conduct studies of heating and cooling strategy, air conditionning or ventilation options, insulating materials to be installed. The main objective of KoZiBu is to forecast the energy consumption, and temperature and humidity evolution range.

 It permits to estimate the instant heating or cooling powers needed to maintain a given set-point, or to calculate the indoor temperatures when the heating or cooling system is insufficient. Humidity is treated in the same way.
It permits to estimate the instant heating or cooling powers needed to maintain a given set-point, or to calculate the indoor temperatures when the heating or cooling system is insufficient. Humidity is treated in the same way.

 KoZiBu can be used to investigate the energy performance of buildings of almost any type and size. In addition to performing peak load calculations necessary for mechanical equipment design, KoZiBu also estimates the annual energy performance of the building.
KoZiBu can be used to investigate the energy performance of buildings of almost any type and size. In addition to performing peak load calculations necessary for mechanical equipment design, KoZiBu also estimates the annual energy performance of the building.

 For more details, see the presented CoDyBa samples.
For more details, see the presented CoDyBa samples.
How does it work
 KoZiBu is based on simply bricks assembled to form a complex building with its equipment. Through the graphical interface, users construct a model of the building's geometry using basic elements (air volumes, walls, windows). Users can add internal loads and HVAC-systems into the created model of the building and perform thermal calculations.
KoZiBu is based on simply bricks assembled to form a complex building with its equipment. Through the graphical interface, users construct a model of the building's geometry using basic elements (air volumes, walls, windows). Users can add internal loads and HVAC-systems into the created model of the building and perform thermal calculations.


 The building main screen is like the Windows Explorer.
The building main screen is like the Windows Explorer.

 The building have to be described accurately : the building description is given by the use of a graphical interface, which includes a building tree, similar to Windows Explorer. Within the interface, each "entity" is associated to a graphical representation, that permits to manipulate it by operations of "copy", "paste", "drag-and-drop" type. The explorer makes it possible to reach and to edit each entity.
The building have to be described accurately : the building description is given by the use of a graphical interface, which includes a building tree, similar to Windows Explorer. Within the interface, each "entity" is associated to a graphical representation, that permits to manipulate it by operations of "copy", "paste", "drag-and-drop" type. The explorer makes it possible to reach and to edit each entity.

 KoZiBu has no limit in air volumes number (thermal zones) : it can simulate building of any size. The only real limit is the time used for the data input.
KoZiBu has no limit in air volumes number (thermal zones) : it can simulate building of any size. The only real limit is the time used for the data input.
The file converter
 As a part of KoZiBu a tool was developed to convert data from other software into CoDyBa or KoZyBu format. The conversion possibilities are described in the following scheme (red for the JNLOG tool, black for another tool provided by CSTB, IZUBA or BBS SLAMA).
As a part of KoZiBu a tool was developed to convert data from other software into CoDyBa or KoZyBu format. The conversion possibilities are described in the following scheme (red for the JNLOG tool, black for another tool provided by CSTB, IZUBA or BBS SLAMA).

 NBDM means "Neutral Building Data Model" (see a sample or posters 1 2). The NBDM project was sponsored by ADEME, French Environment and Energy Management Agency.
NBDM means "Neutral Building Data Model" (see a sample or posters 1 2). The NBDM project was sponsored by ADEME, French Environment and Energy Management Agency.

NFMT is the KoZiBu "neutral language" (see a sample, "Mozart" house from the CSTB typology).

ROWA and TRNSYS are two commercial softwares : ROWA is a tool of the german editor ROWA-Soft and TRNSYS a well-known simulation tool.

Note that the swiss firm PLANCAL realizes an exportation of the data of its CAD software NOVA to the ROWA format.



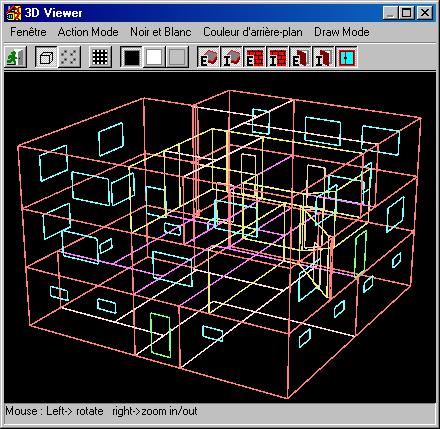
Geometrical data are now integrated in the KoZiBu data model.

The converter makes it possible to extract the geometrical data from the export file of NOVA and to display the shape of the building in a 3D view ('wire' mode for the moment).

The free download version of KoZiBu contains this functionality.
Screen shots
 SEE FURTHER.
SEE FURTHER.
Samples
 Traditional house (1 level, 10 volumes).
Traditional house (1 level, 10 volumes).
 Office building (7 floors, 79 volumes).
Office building (7 floors, 79 volumes).
Audience
 Engineers, researchers, architects, energy consultants (architecture/engineering firms, utilities, equipement manufacturers), students of engineering and architecture.
Engineers, researchers, architects, energy consultants (architecture/engineering firms, utilities, equipement manufacturers), students of engineering and architecture.
Expertise required
 One day of training is desirable but not necessary for those familiar with building modeling.
One day of training is desirable but not necessary for those familiar with building modeling.
Availability
 The single-zone version of CoDyBa (whose successor is KoZiBu) is free (free download).
The single-zone version of CoDyBa (whose successor is KoZiBu) is free (free download).
 The prototype of KoZiBu is currently available for free (free download).
The prototype of KoZiBu is currently available for free (free download).
 Special price for Department of Education and training organisms will be applicable : ½ * Base price.
Special price for Department of Education and training organisms will be applicable : ½ * Base price.
Partnership
 Partners are required to continue the development of KoZiBu (please contact Jean NOEL) :
Partners are required to continue the development of KoZiBu (please contact Jean NOEL) :
 - software developers.
- software developers.
 - researchers and manufacturers : to introduce more sophisticated materials.
- researchers and manufacturers : to introduce more sophisticated materials.
Platform
 PC + Windows.
PC + Windows.
Languages
 KoZiBu is conceived to be multi-languages. The texts are in a separate file, accesible by a text editor : each one can modify them. Currently, only the English and French labels are complete. For German, Spanish and Italian, translators are welcome.
KoZiBu is conceived to be multi-languages. The texts are in a separate file, accesible by a text editor : each one can modify them. Currently, only the English and French labels are complete. For German, Spanish and Italian, translators are welcome.
 The software has been built in an Object-Oriented Programming language : C++ (use of an hierarchy of classes to represent the building).
The software has been built in an Object-Oriented Programming language : C++ (use of an hierarchy of classes to represent the building).
History
 KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa software, which was initially created by J.-J. ROUX, researcher at the University. The version multi-zones of CoDyBa under Windows were carried out by Jean NOEL. La nouvelle version de KoZiBu, avec ses fonctionnalités supplémentaires, est la suite logique de cette histoire.
KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa software, which was initially created by J.-J. ROUX, researcher at the University. The version multi-zones of CoDyBa under Windows were carried out by Jean NOEL. La nouvelle version de KoZiBu, avec ses fonctionnalités supplémentaires, est la suite logique de cette histoire.
Keywords
 Energy simulation, energy efficiency, building performance, renewable energy, comfort, thermal analysis, indoor air temperature, dynamic simulation.
Energy simulation, energy efficiency, building performance, renewable energy, comfort, thermal analysis, indoor air temperature, dynamic simulation.
Other softwares
 You can compare KoZiBu with other software, for example :
DOE2,
TRNSYS,
IDA-ICE,
APACHE,
ESP-r,
PLEIADES-COMFIE.
The points of comparison can be the size of the treated geometries, the scientific tests carried out and published, the treatment of humidity, the number of output graphs, and the price.
You can compare KoZiBu with other software, for example :
DOE2,
TRNSYS,
IDA-ICE,
APACHE,
ESP-r,
PLEIADES-COMFIE.
The points of comparison can be the size of the treated geometries, the scientific tests carried out and published, the treatment of humidity, the number of output graphs, and the price.
Input
 The basic data are the building geometry and constitution : air volumes, walls (with the materials of layers and the surface parameters), windows (possibility for solar masks). The main parameters are : the climate (several meteorological files for different french cities are supplied), internal loads (from lighting, persons, equipments), regulators (powers and set-points for temperature, humidity and ventilation).
The basic data are the building geometry and constitution : air volumes, walls (with the materials of layers and the surface parameters), windows (possibility for solar masks). The main parameters are : the climate (several meteorological files for different french cities are supplied), internal loads (from lighting, persons, equipments), regulators (powers and set-points for temperature, humidity and ventilation).
Output
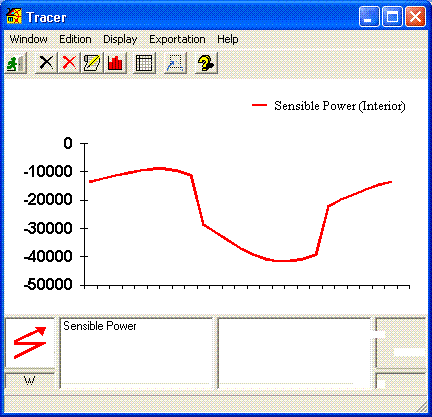
 Some hourly result graphs may be viewed to compare selected alternatives. All result graphs can be exported to other packages such as Microsoft Excel or Word for customised report generation. Following graphical output are available :
Some hourly result graphs may be viewed to compare selected alternatives. All result graphs can be exported to other packages such as Microsoft Excel or Word for customised report generation. Following graphical output are available :
 - building : sensible and latent powers (sum of all air volumes powers).
- building : sensible and latent powers (sum of all air volumes powers).
 - air volumes : sensible and latent powers, indoor air temperature, resultant temperature (average of air and walls temperatures), air relative humidity.
- air volumes : sensible and latent powers, indoor air temperature, resultant temperature (average of air and walls temperatures), air relative humidity.
 - surfaces : absorbed direct and diffuse solar fluxes, surface temperature (useful for thermal comfort evaluation).
- surfaces : absorbed direct and diffuse solar fluxes, surface temperature (useful for thermal comfort evaluation).
 - windows : transmitted direct and diffuse solar fluxes, sunlit fraction, direct and diffuse transmission coefficient, global transmission coefficient g.
- windows : transmitted direct and diffuse solar fluxes, sunlit fraction, direct and diffuse transmission coefficient, global transmission coefficient g.
 - regulators : power.
- regulators : power.
Physical models
Numerical algorithms of KoZiBu are specific, but the physical models of KoZiBu are those commonly admitted :

 Each air volume can contain an unspecified number of temperature regulators (heating/cooling) with their own power and set-point. Power, set-point and activity are given hourly, per day or by week. Humidity is treated in the same way. In the absence of
regulation, the temperature and humidity evolve freely. Regulators have a perfect efficiency.
Each air volume can contain an unspecified number of temperature regulators (heating/cooling) with their own power and set-point. Power, set-point and activity are given hourly, per day or by week. Humidity is treated in the same way. In the absence of
regulation, the temperature and humidity evolve freely. Regulators have a perfect efficiency.
 Taking into account of the mean radiant temperature.
Taking into account of the mean radiant temperature.
 R2C wall model. Wall data is layers (material and thickness), azimuth, tilt, etc.
R2C wall model. Wall data is layers (material and thickness), azimuth, tilt, etc.
 Calculation of each temperature of surface (wall or window), what allows an evaluation of thermal comfort (otherwise very simplified).
Calculation of each temperature of surface (wall or window), what allows an evaluation of thermal comfort (otherwise very simplified).
 The room occupancy is included.
The room occupancy is included.
 Internal loads and regulators can have power or control parameters as time dependent functions.
Internal loads and regulators can have power or control parameters as time dependent functions.
 Taking into account of the absorption coefficients and of emission for each wall.
Taking into account of the absorption coefficients and of emission for each wall.
 Taking into account of the far masks and
shading devices.
Taking into account of the far masks and
shading devices.
 Hour-by-hour weather data is used.
Hour-by-hour weather data is used.
 At present ventilation with outside (in commercial versions).
At present ventilation with outside (in commercial versions).
 Shading devices (venetian blinds, etc.) : a modeling was developed and was tested. A version of KoZiBu
includes this modeling. The results are ready to be published, and a preliminary report (in english) is available.
Shading devices (venetian blinds, etc.) : a modeling was developed and was tested. A version of KoZiBu
includes this modeling. The results are ready to be published, and a preliminary report (in english) is available.

A whole series of functionalities were developed without being integrated into
commercial version (for an use of these functionalities or
for specific studies, consult Jean NOEL) :

 Comfort indices, PPD and PMV (FANGER methods).
Comfort indices, PPD and PMV (FANGER methods).
 Forced aeraulic (flow between air volumes).
Forced aeraulic (flow between air volumes).
Validation
 The BESTEST benchmark (International Energy
Agency) was passed successfully (see report in pdf format). This benchmark is the most precise and the most reliable which exists. Then KoZiBu can simulate the performance of 155 buildings in the BESTEST protocol and in almost all the cases matched the performance of other reference energy programs.
The BESTEST benchmark (International Energy
Agency) was passed successfully (see report in pdf format). This benchmark is the most precise and the most reliable which exists. Then KoZiBu can simulate the performance of 155 buildings in the BESTEST protocol and in almost all the cases matched the performance of other reference energy programs.
 The KoZiBu functionalities described in this web page are not necessary implemented in the current prototype version : only the "converter file" module and partially the "building explorer" are currently available. In fact KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa and the functionalities envisaged will be developed little by little.
The KoZiBu functionalities described in this web page are not necessary implemented in the current prototype version : only the "converter file" module and partially the "building explorer" are currently available. In fact KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa and the functionalities envisaged will be developed little by little. KoZiBu is a design tool on classical PC for buildings dynamic thermal simulation and it's aimed for design offices, teaching and research organisms. The current version may be downloaded for free
KoZiBu is a design tool on classical PC for buildings dynamic thermal simulation and it's aimed for design offices, teaching and research organisms. The current version may be downloaded for free KoZiBu is designed to be multi-languages but currently only French and English are fully implemented, and texts in German, Italian and Spanish are partially translated.
KoZiBu is designed to be multi-languages but currently only French and English are fully implemented, and texts in German, Italian and Spanish are partially translated. KoZiBu is a software used to analyze dynamic hygrothermal performance of building. It is aimed to conduct studies of heating and cooling strategy, air conditionning or ventilation options, insulating materials to be installed. The main objective of KoZiBu is to forecast the energy consumption, and temperature and humidity evolution range.
KoZiBu is a software used to analyze dynamic hygrothermal performance of building. It is aimed to conduct studies of heating and cooling strategy, air conditionning or ventilation options, insulating materials to be installed. The main objective of KoZiBu is to forecast the energy consumption, and temperature and humidity evolution range.
 It permits to estimate the instant heating or cooling powers needed to maintain a given set-point, or to calculate the indoor temperatures when the heating or cooling system is insufficient. Humidity is treated in the same way.
It permits to estimate the instant heating or cooling powers needed to maintain a given set-point, or to calculate the indoor temperatures when the heating or cooling system is insufficient. Humidity is treated in the same way.
 KoZiBu can be used to investigate the energy performance of buildings of almost any type and size. In addition to performing peak load calculations necessary for mechanical equipment design, KoZiBu also estimates the annual energy performance of the building.
KoZiBu can be used to investigate the energy performance of buildings of almost any type and size. In addition to performing peak load calculations necessary for mechanical equipment design, KoZiBu also estimates the annual energy performance of the building.
 For more details, see the presented CoDyBa samples.
For more details, see the presented CoDyBa samples. KoZiBu is based on simply bricks assembled to form a complex building with its equipment. Through the graphical interface, users construct a model of the building's geometry using basic elements (air volumes, walls, windows). Users can add internal loads and HVAC-systems into the created model of the building and perform thermal calculations.
KoZiBu is based on simply bricks assembled to form a complex building with its equipment. Through the graphical interface, users construct a model of the building's geometry using basic elements (air volumes, walls, windows). Users can add internal loads and HVAC-systems into the created model of the building and perform thermal calculations.

 The building main screen is like the Windows Explorer.
The building main screen is like the Windows Explorer.
 The building have to be described accurately : the building description is given by the use of a graphical interface, which includes a building tree, similar to Windows Explorer. Within the interface, each "entity" is associated to a graphical representation, that permits to manipulate it by operations of "copy", "paste", "drag-and-drop" type. The explorer makes it possible to reach and to edit each entity.
The building have to be described accurately : the building description is given by the use of a graphical interface, which includes a building tree, similar to Windows Explorer. Within the interface, each "entity" is associated to a graphical representation, that permits to manipulate it by operations of "copy", "paste", "drag-and-drop" type. The explorer makes it possible to reach and to edit each entity.
 KoZiBu has no limit in air volumes number (thermal zones) : it can simulate building of any size. The only real limit is the time used for the data input.
KoZiBu has no limit in air volumes number (thermal zones) : it can simulate building of any size. The only real limit is the time used for the data input. As a part of KoZiBu a tool was developed to convert data from other software into CoDyBa or KoZyBu format. The conversion possibilities are described in the following scheme (red for the JNLOG tool, black for another tool provided by CSTB, IZUBA or BBS SLAMA).
As a part of KoZiBu a tool was developed to convert data from other software into CoDyBa or KoZyBu format. The conversion possibilities are described in the following scheme (red for the JNLOG tool, black for another tool provided by CSTB, IZUBA or BBS SLAMA).
 NBDM means "Neutral Building Data Model" (see a sample or posters 1 2). The NBDM project was sponsored by ADEME, French Environment and Energy Management Agency.
NBDM means "Neutral Building Data Model" (see a sample or posters 1 2). The NBDM project was sponsored by ADEME, French Environment and Energy Management Agency.
NFMT is the KoZiBu "neutral language" (see a sample, "Mozart" house from the CSTB typology).

ROWA and TRNSYS are two commercial softwares : ROWA is a tool of the german editor ROWA-Soft and TRNSYS a well-known simulation tool.

Note that the swiss firm PLANCAL realizes an exportation of the data of its CAD software NOVA to the ROWA format.




Geometrical data are now integrated in the KoZiBu data model.

The converter makes it possible to extract the geometrical data from the export file of NOVA and to display the shape of the building in a 3D view ('wire' mode for the moment).

The free download version of KoZiBu contains this functionality.
 SEE FURTHER.
SEE FURTHER. Traditional house (1 level, 10 volumes).
Traditional house (1 level, 10 volumes). Office building (7 floors, 79 volumes).
Office building (7 floors, 79 volumes). Engineers, researchers, architects, energy consultants (architecture/engineering firms, utilities, equipement manufacturers), students of engineering and architecture.
Engineers, researchers, architects, energy consultants (architecture/engineering firms, utilities, equipement manufacturers), students of engineering and architecture. One day of training is desirable but not necessary for those familiar with building modeling.
One day of training is desirable but not necessary for those familiar with building modeling. The single-zone version of CoDyBa (whose successor is KoZiBu) is free (free download).
The single-zone version of CoDyBa (whose successor is KoZiBu) is free (free download). The prototype of KoZiBu is currently available for free (free download).
The prototype of KoZiBu is currently available for free (free download). Special price for Department of Education and training organisms will be applicable : ½ * Base price.
Special price for Department of Education and training organisms will be applicable : ½ * Base price. Partners are required to continue the development of KoZiBu (please contact Jean NOEL) :
Partners are required to continue the development of KoZiBu (please contact Jean NOEL) : - software developers.
- software developers. - researchers and manufacturers : to introduce more sophisticated materials.
- researchers and manufacturers : to introduce more sophisticated materials. PC + Windows.
PC + Windows. KoZiBu is conceived to be multi-languages. The texts are in a separate file, accesible by a text editor : each one can modify them. Currently, only the English and French labels are complete. For German, Spanish and Italian, translators are welcome.
KoZiBu is conceived to be multi-languages. The texts are in a separate file, accesible by a text editor : each one can modify them. Currently, only the English and French labels are complete. For German, Spanish and Italian, translators are welcome. The software has been built in an Object-Oriented Programming language : C++ (use of an hierarchy of classes to represent the building).
The software has been built in an Object-Oriented Programming language : C++ (use of an hierarchy of classes to represent the building). KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa software, which was initially created by J.-J. ROUX, researcher at the University. The version multi-zones of CoDyBa under Windows were carried out by Jean NOEL. La nouvelle version de KoZiBu, avec ses fonctionnalités supplémentaires, est la suite logique de cette histoire.
KoZiBu is the successor of CoDyBa software, which was initially created by J.-J. ROUX, researcher at the University. The version multi-zones of CoDyBa under Windows were carried out by Jean NOEL. La nouvelle version de KoZiBu, avec ses fonctionnalités supplémentaires, est la suite logique de cette histoire.  Energy simulation, energy efficiency, building performance, renewable energy, comfort, thermal analysis, indoor air temperature, dynamic simulation.
Energy simulation, energy efficiency, building performance, renewable energy, comfort, thermal analysis, indoor air temperature, dynamic simulation.  You can compare KoZiBu with other software, for example :
DOE2,
TRNSYS,
IDA-ICE,
APACHE,
ESP-r,
PLEIADES-COMFIE.
The points of comparison can be the size of the treated geometries, the scientific tests carried out and published, the treatment of humidity, the number of output graphs, and the price.
You can compare KoZiBu with other software, for example :
DOE2,
TRNSYS,
IDA-ICE,
APACHE,
ESP-r,
PLEIADES-COMFIE.
The points of comparison can be the size of the treated geometries, the scientific tests carried out and published, the treatment of humidity, the number of output graphs, and the price. The basic data are the building geometry and constitution : air volumes, walls (with the materials of layers and the surface parameters), windows (possibility for solar masks). The main parameters are : the climate (several meteorological files for different french cities are supplied), internal loads (from lighting, persons, equipments), regulators (powers and set-points for temperature, humidity and ventilation).
The basic data are the building geometry and constitution : air volumes, walls (with the materials of layers and the surface parameters), windows (possibility for solar masks). The main parameters are : the climate (several meteorological files for different french cities are supplied), internal loads (from lighting, persons, equipments), regulators (powers and set-points for temperature, humidity and ventilation). Some hourly result graphs may be viewed to compare selected alternatives. All result graphs can be exported to other packages such as Microsoft Excel or Word for customised report generation. Following graphical output are available :
Some hourly result graphs may be viewed to compare selected alternatives. All result graphs can be exported to other packages such as Microsoft Excel or Word for customised report generation. Following graphical output are available :  - building : sensible and latent powers (sum of all air volumes powers).
- building : sensible and latent powers (sum of all air volumes powers). - air volumes : sensible and latent powers, indoor air temperature, resultant temperature (average of air and walls temperatures), air relative humidity.
- air volumes : sensible and latent powers, indoor air temperature, resultant temperature (average of air and walls temperatures), air relative humidity. - surfaces : absorbed direct and diffuse solar fluxes, surface temperature (useful for thermal comfort evaluation).
- surfaces : absorbed direct and diffuse solar fluxes, surface temperature (useful for thermal comfort evaluation). - windows : transmitted direct and diffuse solar fluxes, sunlit fraction, direct and diffuse transmission coefficient, global transmission coefficient g.
- windows : transmitted direct and diffuse solar fluxes, sunlit fraction, direct and diffuse transmission coefficient, global transmission coefficient g. - regulators : power.
- regulators : power.
 Each air volume can contain an unspecified number of temperature regulators (heating/cooling) with their own power and set-point. Power, set-point and activity are given hourly, per day or by week. Humidity is treated in the same way. In the absence of
regulation, the temperature and humidity evolve freely. Regulators have a perfect efficiency.
Each air volume can contain an unspecified number of temperature regulators (heating/cooling) with their own power and set-point. Power, set-point and activity are given hourly, per day or by week. Humidity is treated in the same way. In the absence of
regulation, the temperature and humidity evolve freely. Regulators have a perfect efficiency. Taking into account of the mean radiant temperature.
Taking into account of the mean radiant temperature. R2C wall model. Wall data is layers (material and thickness), azimuth, tilt, etc.
R2C wall model. Wall data is layers (material and thickness), azimuth, tilt, etc. Calculation of each temperature of surface (wall or window), what allows an evaluation of thermal comfort (otherwise very simplified).
Calculation of each temperature of surface (wall or window), what allows an evaluation of thermal comfort (otherwise very simplified). The room occupancy is included.
The room occupancy is included. Internal loads and regulators can have power or control parameters as time dependent functions.
Internal loads and regulators can have power or control parameters as time dependent functions. Taking into account of the absorption coefficients and of emission for each wall.
Taking into account of the absorption coefficients and of emission for each wall. Taking into account of the far masks and
shading devices.
Taking into account of the far masks and
shading devices. Hour-by-hour weather data is used.
Hour-by-hour weather data is used. At present ventilation with outside (in commercial versions).
At present ventilation with outside (in commercial versions). Shading devices (venetian blinds, etc.) : a modeling was developed and was tested. A version of KoZiBu
includes this modeling. The results are ready to be published, and a preliminary report (in english) is available.
Shading devices (venetian blinds, etc.) : a modeling was developed and was tested. A version of KoZiBu
includes this modeling. The results are ready to be published, and a preliminary report (in english) is available.
A whole series of functionalities were developed without being integrated into commercial version (for an use of these functionalities or for specific studies, consult Jean NOEL) :

 Comfort indices, PPD and PMV (FANGER methods).
Comfort indices, PPD and PMV (FANGER methods). Forced aeraulic (flow between air volumes).
Forced aeraulic (flow between air volumes). The BESTEST benchmark (International Energy
Agency) was passed successfully (see report in pdf format). This benchmark is the most precise and the most reliable which exists. Then KoZiBu can simulate the performance of 155 buildings in the BESTEST protocol and in almost all the cases matched the performance of other reference energy programs.
The BESTEST benchmark (International Energy
Agency) was passed successfully (see report in pdf format). This benchmark is the most precise and the most reliable which exists. Then KoZiBu can simulate the performance of 155 buildings in the BESTEST protocol and in almost all the cases matched the performance of other reference energy programs.

 Wall.
Wall. Window.
Window.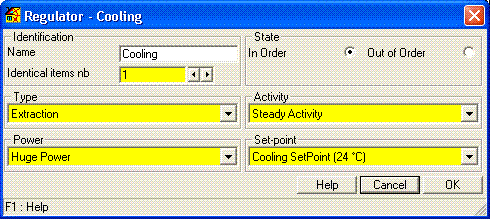 Cooling.
Cooling. Lighting.
Lighting.